- All Exams Instant Download
Which of the following statements are true regarding Amazon VPC subnets?
An aerospace engineering company recently adopted a hybrid cloud infrastructure with AWS. One of the Solutions Architect’s tasks is to launch a VPC with both public and private subnets for their EC2 instances as well as their database instances.
Which of the following statements are true regarding Amazon VPC subnets? (Select TWO.)
A . Every subnet that you create is automatically associated with the main route table for the VP
C . The allowed block size in VPC is between a /16 netmask (65,536 IP addresses) and /27 netmask (32 IP addresses).
D . Each subnet spans to 2 Availability Zones.
E . Each subnet maps to a single Availability Zone.
F . EC2 instances in a private subnet can communicate with the Internet only if they have an Elastic I
Answer: A,D
Explanation:
A VPC spans all the Availability Zones in the region. After creating a VPC, you can add one or more subnets in each Availability Zone. When you create a subnet, you specify the CIDR block for the subnet, which is a subset of the VPC CIDR block. Each subnet must reside entirely within one Availability Zone and cannot span zones. Availability Zones are distinct locations that are engineered to be isolated from failures in other Availability Zones. By launching instances in separate Availability Zones, you can protect your applications from the failure of a single location.
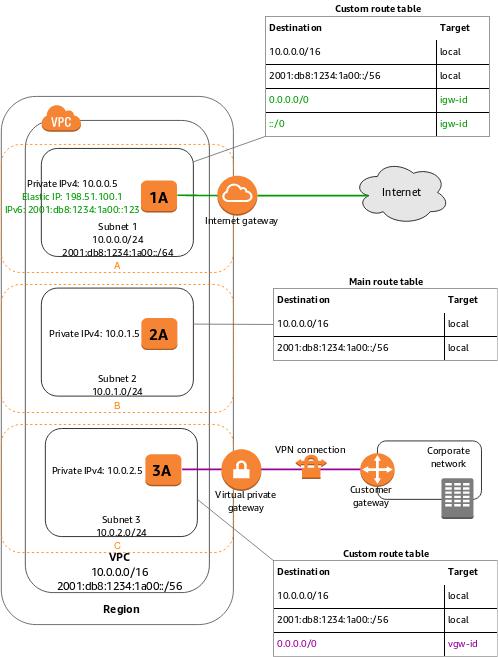
Below are the important points you have to remember about subnets:
– Each subnet maps to a single Availability Zone.
– Every subnet that you create is automatically associated with the main route table for the VPC.
– If a subnet’s traffic is routed to an Internet gateway, the subnet is known as a public subnet.
The option that says: EC2 instances in a private subnet can communicate with the Internet only if they have an Elastic IP is incorrect. EC2 instances in a private subnet can communicate with the Internet not just by having an Elastic IP, but also with a public IP address via a NAT Instance or a NAT Gateway. Take note that there is a distinction between private and public IP addresses. To enable communication with the Internet, a public IPv4 address is mapped to the primary private IPv4 address through network address translation (NAT).
The option that says: The allowed block size in VPC is between a /16 netmask (65,536 IP addresses) and /27 netmask (32 IP addresses) is incorrect because the allowed block size in VPC is between a /16 netmask (65,536 IP addresses) and /28 netmask (16 IP addresses) and not /27 netmask.
The option that says: Each subnet spans to 2 Availability Zones is incorrect because each subnet must reside entirely within one Availability Zone and cannot span zones. References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonVPC/latest/UserGuide/VPC_Subnets.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/vpc-ip-addressing.html Check out this Amazon VPC Cheat Sheet: https://tutorialsdojo.com/amazon-vpc/
Tutorials Dojo’s AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Exam Study Guide:
https://tutorialsdojo.com/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/
Latest SAA-C03 Dumps Valid Version with 400 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Inline Feedbacks
View all comments

