- All Exams Instant Download
Which of the following should you do to meet the above requirement?
An organization stores and manages financial records of various companies in its on-premises data center, which is almost out of space. The management decided to move all of their existing records to a cloud storage service. All future financial records will also be stored in the cloud. For additional security, all records must be prevented from being deleted or overwritten .
Which of the following should you do to meet the above requirement?
A . Use AWS DataSync to move the data. Store all of your data in Amazon S3 and enable object lock.
B . Use AWS Storage Gateway to establish hybrid cloud storage. Store all of your data in Amazon S3 and enable object lock.
C . Use AWS Storage Gateway to establish hybrid cloud storage. Store all of your data in Amazon EBS and enable object lock.
D . Use AWS DataSync to move the data. Store all of your data in Amazon EFS and enable object lock.
Answer: A
Explanation:
AWS DataSync allows you to copy large datasets with millions of files, without having to build custom solutions with open source tools, or license and manage expensive commercial network acceleration software. You can use DataSync to migrate active data to AWS, transfer data to the cloud for analysis and processing, archive data to free up on-premises storage capacity, or replicate data to AWS for business continuity.
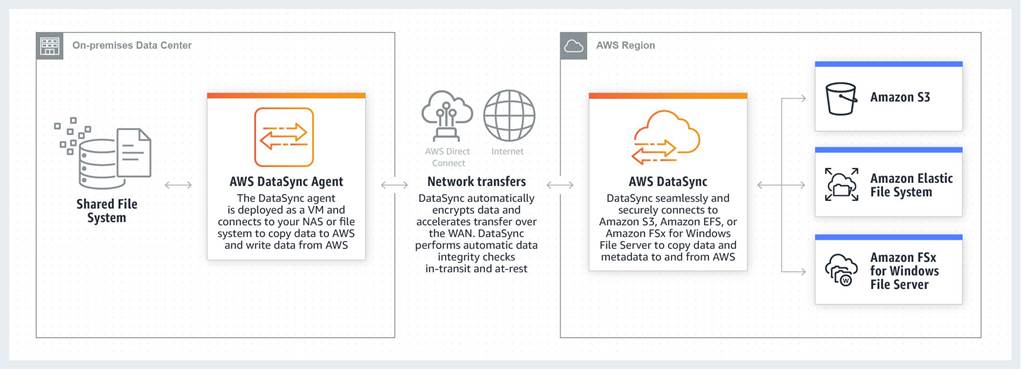
AWS DataSync enables you to migrate your on-premises data to Amazon S3, Amazon EFS, and Amazon FSx for Windows File Server. You can configure DataSync to make an initial copy of your entire dataset, and schedule subsequent incremental transfers of changing data towards Amazon S3. Enabling S3 Object Lock prevents your existing and future records from being deleted or overwritten.
AWS DataSync is primarily used to migrate existing data to Amazon S3. On the other hand, AWS Storage Gateway is more suitable if you still want to retain access to the migrated data and for ongoing updates from your on-premises file-based applications.
Hence, the correct answer in this scenario is: Use AWS DataSync to move the data. Store all of your data in Amazon S3 and enable object lock.
The option that says: Use AWS DataSync to move the data. Store all of your data in Amazon EFS and enable object lock is incorrect because Amazon EFS only supports file locking. Object lock is a feature of Amazon S3 and not Amazon EFS.
The options that says: Use AWS Storage Gateway to establish hybrid cloud storage. Store all of your data in Amazon S3 and enable object lock is incorrect because the scenario requires that all of the existing records must be migrated to AWS. The future records will also be stored in AWS and not in the on-premises network. This means that setting up a hybrid cloud storage is not necessary since the on-premises storage will no longer be used.
The option that says: Use AWS Storage Gateway to establish hybrid cloud storage. Store all of your data
in Amazon EBS and enable object lock is incorrect because Amazon EBS does not support object lock.
Amazon S3 is the only service capable of locking objects to prevent an object from being deleted or
overwritten.
References:
https://aws.amazon.com/datasync/faqs/ https://docs.aws.amazon.com/datasync/latest/userguide/what-is-datasync.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/object-lock.html Check out this AWS DataSync Cheat Sheet:
https://tutorialsdojo.com/aws-datasync/
AWS Storage Gateway vs DataSync:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tmfe1rO-AUs
Amazon S3 vs EBS vs EFS Cheat Sheet:
https://tutorialsdojo.com/amazon-s3-vs-ebs-vs-efs/
Latest SAA-C03 Dumps Valid Version with 400 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Inline Feedbacks
View all comments

