Which Microsoft Azure Power Shell cmdlet should you use with each Power Shell command line?
DRAG DROP
You manage an Azure virtual machine (VM) named AppVM. The application hosted on AppVM continuously writes small files to disk. Recently the usage of applications on AppVM has increased greatly.
You need to improve disk performance on AppVM.
Which Microsoft Azure Power Shell cmdlet should you use with each Power Shell command line? To answer, drag the appropriate Microsoft Azure Power Shell cmdlet to the correct location in the Power Shell code. Each Power Shell cmdlet may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
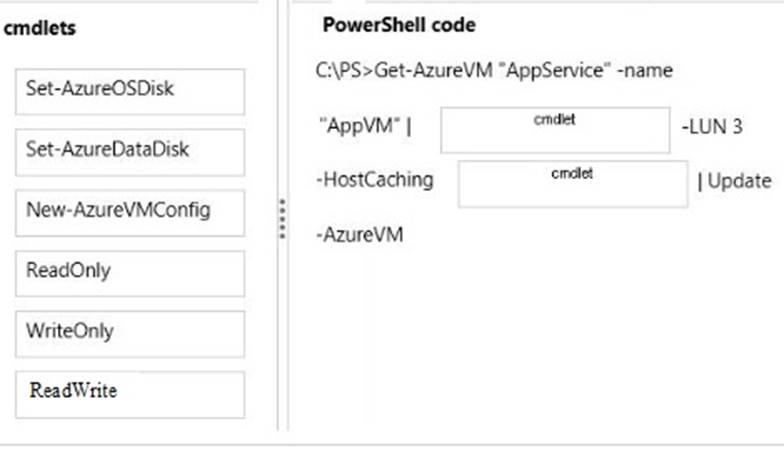
Answer: 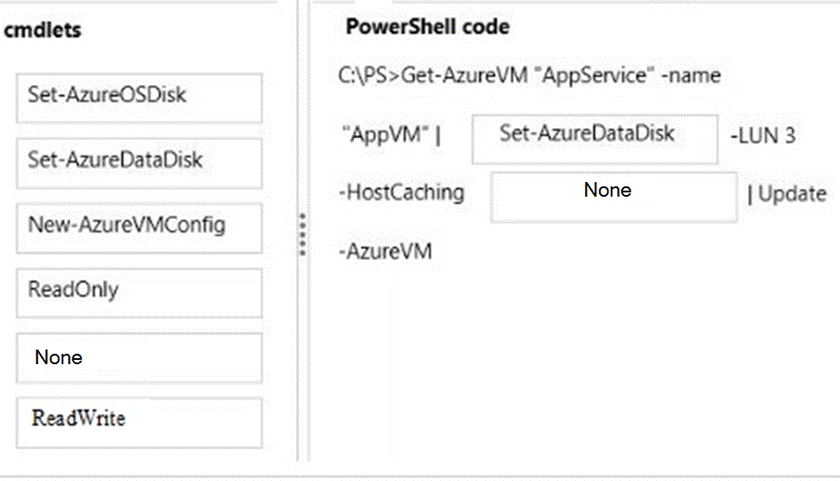
Explanation:
* Set-AzureDataDisk
Sets the host-cache mode on an existing data disk object.
* Example:
This command gets the "MyVM" virtual machine running on the "myservice" cloud service, and then sets the data disk at LUN 2 of the virtual machine to use Nonehost caching.
Windows PowerShell
C:PS>Get-AzureVM "myservice" -name "MyVM" | Set-AzureDataDisk -LUN 2 -HostCachingNone| Update-AzureVM
* Set-AzureDataDisk Parameter: -HostCaching<String>
Sets the host level caching settings of the disk. Possible values are: None, ReadOnly and ReadWrite ().
When you setup a data disk on a virtual machine, you get three host caching choices:
The purpose of a cache is to cache data to be read as reading from a cache is faster than reading from a disk.
There is no performance benefit in caching the log files as these will not be re-read by the application. Therefore, we need the logs to be written directly to disks rather than being written to cache first then disk (Read) or written to the cache only (Read/Write).
Latest 70-533 Dumps Valid Version with 351 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

