- All Exams Instant Download
Which Spanning Tree Protocol should be used to reduce switch resources and managerial burdens that are associated with multiple spanning-tree instances?
A network engineer is setting up a new switched network. The network is expected to grow and add many new VLANs in the future.
Which Spanning Tree Protocol should be used to reduce switch resources and managerial burdens that are associated with multiple spanning-tree instances?
A . RSTP
B . PVST
C . MST
D . PVST+
E . RPVST+
Answer: C
Explanation:
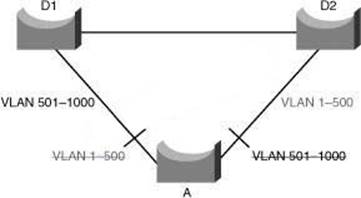
Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) extends the IEEE 802.1w RST algorithm to multiple spanning trees. The main purpose of MST is to reduce the total number of spanning-tree instances to match the physical topology of the network and thus reduce the CPU cycles of a switch. PVRST+ runs STP instances for each VLAN and does not take into consideration the physical topology that might not require many different STP topologies. MST, on the other hand, uses a minimum number of STP instances to match the number of physical topologies present. Figure 3-15 shows a common network design, featuring an access Switch A, connected to two Building Distribution submodule Switches D1 and D2. In this setup, there are 1000 VLANs, and the network administrator typically seeks to achieve load balancing on the access switch uplinks based on even or odd VLANs–or any other scheme deemed appropriate.
Figure 3-15: VLAN Load Balancing Figure 3-15 illustrates two links and 1000 VLANs. The 1000 VLANs map to two MST instances. Rather than maintaining 1000 spanning trees, each switch needs to maintain only two spanning trees, reducing the need for switch resources. Reference: http://ciscodocuments.blogspot.com/2011/05/chapter-03-implementing-spanning- tree_19.html
Latest 300-115 Dumps Valid Version with 342 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Inline Feedbacks
View all comments

