- All Exams Instant Download
Given this scenario, which of the following should the administrator do to recover this volume?
One leg of an LVM-mirrored volume failed due to the underlying physical volume, and a systems administrator is troubleshooting the issue.
The following output has been provided:
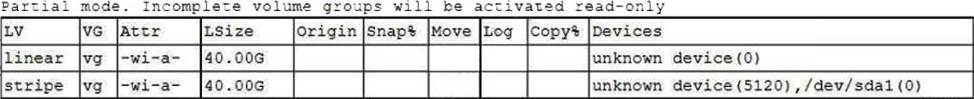
Given this scenario, which of the following should the administrator do to recover this volume?
A . Reboot the server. The volume will automatically go back to linear mode.
B . Replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror.
C . Reboot the server. The volume will revert to stripe mode.
D . Recreate the logical volume.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The administrator should replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror to recover the volume. The LVM (Logical Volume Manager) is a tool for managing disk space on Linux systems. The LVM allows the administrator to create logical volumes that span across multiple physical volumes, such as hard disks or partitions. The LVM also supports different types of logical volumes, such as linear, striped, or mirrored. A mirrored logical volume is a type of logical volume that creates a copy of the data on another physical volume, providing redundancy and fault tolerance. The output shows that the logical volume is mirrored and that one leg of the mirror has failed due to the underlying physical volume. This means that one of the physical volumes that contains the data of the logical volume is damaged or missing. This can cause data loss and performance degradation. The administrator should replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror to recover the volume. The administrator should identify the failed physical volume by using commands such as pvdisplay, vgdisplay, or lvdisplay. The administrator should then remove the failed physical volume from the volume group by using the vgreduce command. The administrator should then install a new drive and create a new physical volume by using the pvcreate command. The administrator should then add the new physical volume to the volume group by using the vgextend command. The administrator should then reconfigure the mirror by using the lvconvert command. The administrator should replace the failed drive and reconfigure the mirror to recover the volume. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they either do not recover the volume (reboot the server. The volume will automatically go back to linear mode or reboot the server. The volume will revert to stripe mode) or do not preserve the data of the volume (recreate the logical volume).
References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, pages 333-334.
Latest XK0-005 Dumps Valid Version with 136 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Inline Feedbacks
View all comments

