Splunk SPLK-1003 Splunk Enterprise Certified Admin Online Training
Splunk SPLK-1003 Online Training
The questions for SPLK-1003 were last updated at Jun 21,2025.
- Exam Code: SPLK-1003
- Exam Name: Splunk Enterprise Certified Admin
- Certification Provider: Splunk
- Latest update: Jun 21,2025
Which of the following is valid distribute search group?
A)

B)
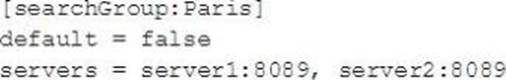
C)
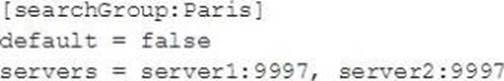
D)
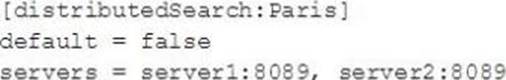
- A . option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
Local user accounts created in Splunk store passwords in which file?
- A . $ SFLUNK_HOME/etc/passwd
- B . $ SFLUNK_HOME/etc/authentication
- C . $ SPLUNK_HOME/etc/users/passwd.conf
- D . $ SPLUNK HOME/etc/users/authentication.conf
A
Explanation:
Per the provided reference URL https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/7.3.1/Admin/User-seedconf
"To set the default username and password, place user-seed.conf in
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local. You must restart Splunk to enable configurations. If the
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/passwd file is present, the settings in this file (user-seed.conf) are not used."
For single line event sourcetypes. it is most efficient to set SHOULD_linemerge to what value?
- A . True
- B . False
- C . <regex string>
- D . Newline Character
B
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/Data/Configureeventlinebreaking
Attribute: SHOULD_LINEMERGE = [true|false]
Description: When set to true, the Splunk platform combines several input lines into a single event, with configuration based on the settings described in the next section.
Which Splunk component does a search head primarily communicate with?
- A . Indexer
- B . Forwarder
- C . Cluster master
- D . Deployment server
Which layers are involved in Splunk configuration file layering? (select all that apply)
- A . App context
- B . User context
- C . Global context
- D . Forwarder context
ABC
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/Admin/Wheretofindtheconfigurationfiles
To determine the order of directories for evaluating configuration file precedence, Splunk software considers each file’s context. Configuration files operate in either a global context or in the context of the current app and user: Global. Activities like indexing take place in a global context. They are independent of any app or user. For example, configuration files that determine monitoring or indexing behavior occur outside of the app and user context and are global in nature. App/user. Some activities, like searching, take place in an app or user context. The app and user context is vital to search-time processing, where certain knowledge objects or actions might be valid only for specific users in specific apps.
Which of the following are methods for adding inputs in Splunk? (select all that apply)
- A . CLI
- B . Splunk Web
- C . Editing inputs. conf
- D . Editing monitor. conf
ABC
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.2.2/Data/Configureyourinputs
Add your data to Splunk Enterprise. With Splunk Enterprise, you can add data using Splunk Web or Splunk Apps. In addition to these methods, you also can use the following methods. -The Splunk Command Line Interface (CLI) -The inputs.conf configuration file. When you specify your inputs with Splunk Web or the CLI, the details are saved in a configuartion file on Splunk Enterprise indexer and heavy forwarder instances.
Which of the following authentication types requires scripting in Splunk?
- A . ADFS
- B . LDAP
- C . SAML
- D . RADIUS
D
Explanation:
https://answers.splunk.com/answers/131127/scripted-authentication.html
Scripted Authentication: An option for Splunk Enterprise authentication. You can use an authentication system that you have in place (such as PAM or RADIUS) by configuring authentication.conf to use a script instead of using LDAP or Splunk Enterprise default authentication.
Which option accurately describes the purpose of the HTTP Event Collector (HEC)?
- A . A token-based HTTP input that is secure and scalable and that requires the use of forwarders
- B . A token-based HTTP input that is secure and scalable and that does not require the use of forwarders.
- C . An agent-based HTTP input that is secure and scalable and that does not require the use of forwarders.
- D . A token-based HTTP input that is insecure and non-scalable and that does not require the use of forwarders.
B
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.2.2/Data/UsetheHTTPEventCollector
"The HTTP Event Collector (HEC) lets you send data and application events to a Splunk deployment over the HTTP and Secure HTTP (HTTPS) protocols. HEC uses a token-based authentication model. You can generate a token and then configure a logging library or HTTP client with the token to send data to HEC in a specific format. This process eliminates the need for a Splunk forwarder when you send application events."
What is the difference between the two wildcards … and – for the monitor stanza in inputs, conf?
- A . … is not supported in monitor stanzas
- B . There is no difference, they are interchangable and match anything beyond directory boundaries.
- C . * matches anything in that specific directory path segment, whereas … recurses through subdirectories as well.
- D . … matches anything in that specific directory path segment, whereas – recurses through subdirectories as well.
C
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/7.3.0/Data/Specifyinputpathswithwildcards
… The ellipsis wildcard searches recursively through directories and any number of levels of subdirectories to find matches.
If you specify a folder separator (for example, //var/log/…/file), it does not match the first folder level, only subfolders.
* The asterisk wildcard matches anything in that specific folder path segment. Unlike …, * does not recurse through subfolders.
What type of data is counted against the Enterprise license at a fixed 150 bytes per event?
- A . License data
- B . Metricsdata
- C . Internal Splunk data
- D . Internal Windows logs
Latest SPLK-1003 Dumps Valid Version with 119 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

