BICSI RCDD-002 BICSI Registered Communications Distribution Designer – RCDD Online Training
BICSI RCDD-002 Online Training
The questions for RCDD-002 were last updated at Jul 19,2025.
- Exam Code: RCDD-002
- Exam Name: BICSI Registered Communications Distribution Designer - RCDD
- Certification Provider: BICSI
- Latest update: Jul 19,2025
A backbone star topology shall have no more than______ level(s) of cross-connections.
- A . One
- B . Two
- C . Three
- D . Four
- E . Five
Rack mounted hardware is installed in two standard sized racks or cabinets. Those sizes are:
- A . 482 mm (19 in) and 584 mm (23 in)
- B . 482 mm (19 in) and 762 mm (30 in)
- C . 610 mm (24 in) and 762 mm (30 in)
- D . 762 mm (30 in) and 914 mm (36 in)
- E . 482 mm (19 in) and 1020 mm (40 in)
Exhibit:
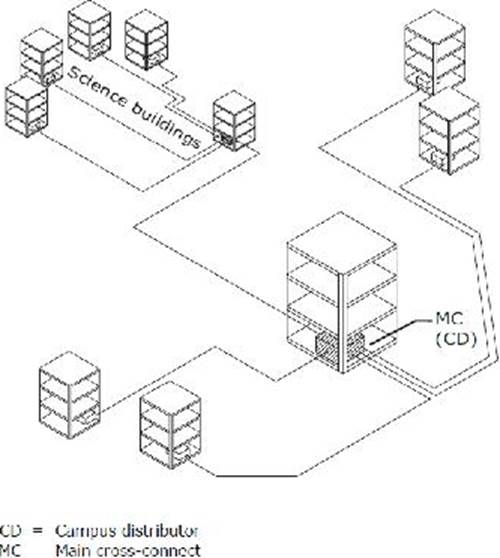
This diagram illustrates an example of a:
- A . Multiple one level backbone designs
- B . Multiple hierarchical level campus backbone design
- C . Poorly designed single level campus backbone design
- D . Well laid out single level campus backbone design
- E . Multi level campus design ready for an easy separation into 3 single level designs
One of the advantages of using optical fiber in the backbone installation is:
- A . More cost effective
- B . Immunity to EMI
- C . Safer to install
- D . Requires less skill to install
- E . Has better manufacturer support
When designing a backbone distribution system, you are asked to include a combination of media types.
Your choice of media types include:
- A . Copper and fiber only
- B . Fiber and wireless only
- C . Fiber and coaxial cable only
- D . Wireless and coaxial cable only
- E . Any combination of copper, fiber, and wireless
An installation crew is pulling an optical fiber cable into a riser. The cable has an outside diameter of 25 mm (1 in). As the cable is being pulled off the reel and through a pulley into the riser, you must verify that the minimum bend radius for the cable being pulled is observed.
The pulley must be sized at a MINIMUM of:
- A . 254 mm (10 in)
- B . 381 mm (15 in)
- C . 508 mm (20 in)
- D . 635 mm (25 in)
- E . 762 mm (30 in)
Exhibit:
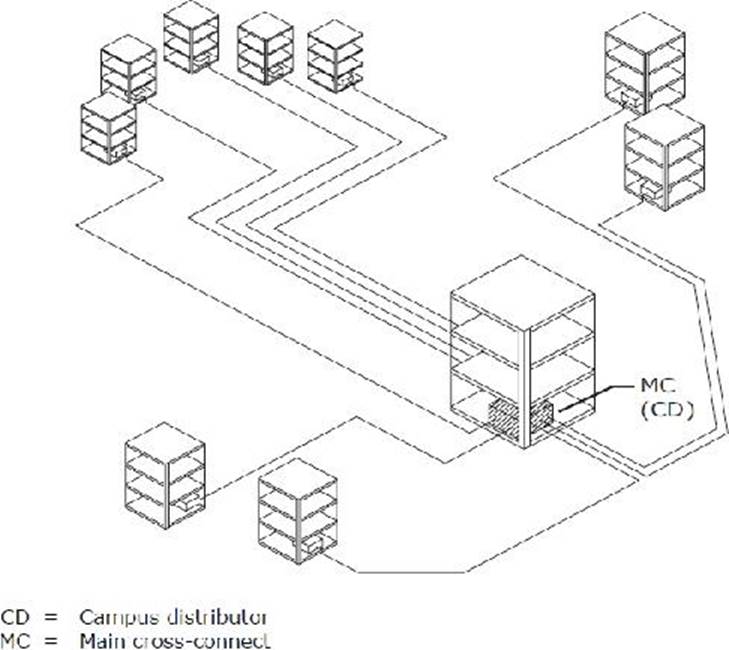
This diagram illustrates a ______________campus backbone design.
- A . Hierarchical star
- B . Ring topology
- C . Bus topology
- D . Inverted star
- E . Collapsed ring
In the customer’s environment, an ITS designer should avoid the need for optical fiber field splicing by:
- A . Installing oversized inner duct
- B . Using oversized cable trays
- C . Using pre-connectorized cables
- D . Installing a continuous length of cable
- E . Using multiple pull boxes
When designing a fiber backbone using cable with an armored sheath, a major consideration that you must address is:
- A . Type of metal used in the sheath
- B . Strength of the armored sheath
- C . Amount of aluminum contained in the armored sheath
- D . Amount of steel in the sheath as rust is an issue
- E . Bonding and grounding of the armored sheath
You are reviewing a building backbone design with a vertically aligned telecommunications room (TR). In the spec you note in a footnote with details that the slots at one end of the telecommunications room (TR) must be flush with the floor and the sleeves provide at the end of the telecommunications room (TR) must also be flush.
In your meeting with the electrical engineering firm that has provided the spec, you make the comment that according to best practices, the MINIMUM that slots and sleeves must extend above the finished floor are:
- A . 25 mm (1 in) for slots and 51 mm (2 in)
- B . 25 mm (1 in) for slots and 25 mm (1 in)
- C . 51 mm (2 in) for slots and 25 mm (1 in)
- D . 51 mm (2 in) for slots and 51 mm (2 in)
- E . 64 mm (2 1/2 in) for slots and 64 mm (2 1/2 in)
Latest RCDD-002 Dumps Valid Version with 361 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

