Which of the following would NOT occur during sympathetic stimulation?
- A . secretion of glucagon
- B . dilation of bronchioles
- C . dilation of intestinal blood vessels
- D . dilation of pupils
C
Explanation:
The blood flow to visceral organs decreases during sympathetic stimulation, but increases under parasympathetic stimulation. One function of the sympathetic nervous system is to increase blood flow to organs in demand of air or nutrients. During the fight-or-flight response, vasodilation works to move blood away from the digestive system and towards the muscles.
Which of the following would increase the pH of the blood?
- A . severe damage to the kidneys
- B . the digestion of a big meal
- C . an increase in anaerobic respiration
- D . an increase of the blood pCO2
B
Explanation:
During the digestion of a large meal, parietal cells in the stomach generate hydrochloric acid (HCl) in exchange for a bicarbonate ion which enters the blood plasma, increasing the pH.
Which of the following yields the least ATP directly?
- A . TCA cycle
- B . oxidative phosphorylation
- C . glycolysis
- D . Beta Oxidation
A
Explanation:
The TCA cycle yields 2 GTPs (molecules that can be converted to ATP but are not ATP themselves), oxidative phosphorylation, which includes the ETC, can yield from 32 to 34 ATP. Glycolysis yields 2 ATP. Beta oxidation yields a range over 100 ATP that depends on the length of the fatty acid being degraded.
The T-tubules transmit an action potential, causing the opening of ____ channels in the ____.
- A . Na+, Sarcoplasm
- B . Ca2+, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- C . Na+, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- D . Ca2+, Sarcoplasm
B
Explanation:
The T-tubules conduct action potentials that cause channels to open on the surface of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The opening of these channels results in a release of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasm of the muscle fiber.
Which of the following decompose disaccharides into monosaccharides?
- A . salivary amylase
- B . pancreatic enzymes
- C . gastrin
- D . brush border enzymes
D
Explanation:
Disaccharides such as sucrose, maltose, and lactose, etc., are broken down further into monosaccharides (primarily glucose) in the small intestine by way of brush border enzymes lining microvilli of the small intestine.
Which of the following does hemoglobin bond most strongly with?
- A . oxygen
- B . carbon dioxide
- C . carbon monoxide
- D . hydrogen
C
Explanation:
Hemoglobin bonds most strongly with carbon monoxide as a result of the interaction of the orbitals of the hemoglobin and the carbon monoxide molecule. The carbon forms an ionic bond with the hemoglobin’s iron, and because of the joint configuration, the iron is able to donate additional electrons to the carbon monoxide.
Which of the following is not secreted by the hypothalamus?
- A . glucocorticoids
- B . GnRH
- C . Dopamine
- D . GHIH
A
Explanation:
Glucocorticoids are steroids synthesized and secreted by the adrenal cortex not the hypothalamus.
A virulent phage is one which infects via:
- A . the lysogenic cycle
- B . phagocytosis
- C . immunoglobins
- D . the lytic cycle
D
Explanation:
Virulent phages use the lytic cycle to infect an organism. The lytic cycle is the process by which a phage DNA replicates itself via the host cell before causing the cell to lyse and release all of the phage’s replications.
Which is not a function of immunoglobins?
- A . coagulation
- B . assist in phagocytosis
- C . attack pathogens
- D . labeling of pathogens
C
Explanation:
Antibodies or immunoglobins perform all of the functions except for directly attacking pathogens. Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are responsible for attacking pathogens.
What results in extra or fewer chromosomes in a cell?
- A . nondisjunction
- B . double replication
- C . double cytokinesis
- D . epistasis
A
Explanation:
Nondisjunction is when chromosomes do NOT separate during anaphase. Consequently, the resulting cells display an unequal sharing of chromosomes, with some cells having too many, and others having too few.
For vision, ___ must be converted to _____ in the cells of the retina.
- A . vitamin C, retinal
- B . vitamin E, biotin
- C . vitamin A, retinal
- D . vitamin A, biotin
C
Explanation:
Vitamin A is a precursor of retinal, which is the chemical compound that enables animals to see. Biotin is associated with vitamin B. Carrots are known to be good for vision because they are high in vitamin A.
Which of the following is involved in hearing?
- A . microvilli
- B . cilia
- C . hair follicles
- D . hair cells
D
Explanation:
Hair cells lining the basilar membrane utilize mechanotransduction to detect, to amplify, and to convert mechanical sound waves into electrical signals. The resulting action potential then passes through the cochlear nerve to reach the brain.
Which is not active in bone resorption?
- A . osteoblasts
- B . osteoclasts
- C . nephrons
- D . small intestine
A
Explanation:
Bone resorption, the decomposition of bone for absorption of minerals, including calcium, directly involves osteoclasts. Nephrons and the small intestine both absorb released Ca2+. Osteoblasts function to construct, not decompose, bones.
Which of the following will result if there is a drop-in blood pressure?
- A . formation of glucose
- B . secretion of insulin
- C . secretion of EPO
- D . secretion of ANP
C
Explanation:
A drop-in blood pressure causes the renal cortex of the kidney to secrete EPO (erythropoietin) in an effort to increase the blood pressure by increasing the synthesis of red blood cells. EPO is a necessary precursor for red blood cell production to take place.
Which of the following occurs as a rise in intraocular pressure?
- A . inflammation of the cornea
- B . glaucoma
- C . cataract
- D . diabetic retinopathy
B
Explanation:
Intraocular pressure (IOP) poses the greatest risk of causing glaucoma. A reduction in the flow and drainage of aqueous humor leads to a rise in IOP. The built-up pressure eventually results in glaucoma and optic nerve damage.
In which non-membranous compartment are ribosomes made in a eukaryotic cell?
- A . nucleus
- B . rough ER
- C . nucleolus
- D . cytoplasm
C
Explanation:
Ribosomes are manufactured inside of the nucleolus. RNA polymerases I and III work together to create ribosomes from rRNA and proteins.
Which of the following lists the correct taxonomic order from most inclusive to least inclusive?
- A . Kingdom, Order, Class, Species
- B . Order, Family, Genus, Phylum
- C . Order, Family, Genus, Species
- D . Phylum, Order, Species, Genus
C
Explanation:
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species. The mnemonic, “King Philip Came Over For Great Spaghetti,” is very useful for remembering the taxonomic order from most inclusive to least inclusive.
Which of the following corresponds to the coding strand of the following mRNA?
5’-GUAACGUCA- 3’
- A . 5’-GTAACGTCA-3’
- B . 5’-CATTGCAGT-3’
- C . 5’-ACUGCAAUG- 3’
- D . 5’-TGACGTTAC- 3’
A
Explanation:
The coding strand is NOT the complementary strand; it is the strand of DNA which is complementary to the strand from which mRNA is made. The coding strand will have the same sequence of bases as the produced RNA transcript except with thymine instead of uracil. A useful mnemonic for remembering the nucleotide bases in DNA and RNA is “GCAT PuPy” and “GCAU PuPy.” GCAT/U stand for guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine, and uracil, and “Pu” and “Py” represent purine and pyrimidine, respectively.
Which cells make up the insulated wrapping on axons?
- A . Schwann cells
- B . astrocytes
- C . microglia
- D . macrocytes
A
Explanation:
Axons are surrounded by insulating cells called Schwann cells. This insulation enables action potentials to travel rapidly throughout the nervous system.
Which of the following statements regarding energy production is true?
- A . There is a net total of 4 ATP produced in glycolysis.
- B . The GTP made in the TCA cycle does not become ATP.
- C . The cell requires energy to move NADH into the mitochondria.
- D . The net gain of ATP from each NADH is 2.
C
Explanation:
Transport of the NADH into the mitochondria in most cases requires 1 ATP. This is the reason that prokaryotes often have a higher yield of ATP per glucose when compared to eukaryotes. Usually 38 ATP are produced per glucose for prokaryotes, and 36 per glucose for eukaryotes.
Blood flows from the mitral valve to the:
- A . left atrium
- B . aorta
- C . right ventricle
- D . left ventricle
D
Explanation:
The left atrium connects to the left ventricle by way of the mitral valve. The left ventricle connects to the aorta by way of the aortic valve. Blood flows from the pulmonary veins into the left atrium and through the mitral valve (bicuspid valve), to the left ventricle then out through the aorta.
A female who is a carrier of an X-linked recessive disability produces an offspring with a normal male.
What is the chance that the male offspring will have the disability?
- A . 0%
- B . 25%
- C . 50%
- D . 100%
C
Explanation:
The situation presented is an Xx (female) crossed with an XY (male). Because the offspring is a male (XY), the X-chromosome must come from the mother. Consequently, there is a 50% chance of receiving the recessive x-chromosome.
Energy for ATP synthesis is produced primarily by:
- A . NADH
- B . proton gradient
- C . ATP synthase
- D . Na+
B
Explanation:
Proton pumps located along the inner mitochondrial membrane enable the passage of H+ across a concentration gradient. These protons pass through ATP synthase in which an axel rotates to combine phosphate with ADP to form ATP. Without the proton gradient, ATP synthase could not create ATP.
Which of the listed antibodies is released in response to an allergen?
- A . IgA
- B . IgE
- C . IgG
- D . IgM
B
Explanation:
IgE is the antibody primarily involved in allergic reactions.
A cross between red bean (RR) and a blue bean (UU) yields all purple beans.
How many purple beans would result from a cross between two purple beans?
- A . 0.25 of the offspring
- B . 0.50 of the offspring
- C . 0.75 of the offspring
- D . all of the offspring
B
Explanation:
Begin by crossing a red bean with a blue bean: RR × UU gives all RU, also known as incomplete dominance. Next cross a purple bean with a purple bean: RU × RU yields 1 RR, 2 RU and 1 UU. Two out of the four offspring are purple beans. This is the same as 0.50, or 50%.
The release of ____ into the blood would increase the heart rate.
- A . rennin
- B . ANP
- C . norepinephrine
- D . insulin
C
Explanation:
Norepinephrine (as well as epinephrine), released by the adrenal glands, stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. A consequence of norepinephrine and epinephrine on the heart is an increase in the heart rate. The sympathetic nervous system is linked to the fight-or-flight response.
Which of the following is NOT the result of a viral infection?
- A . genital warts
- B . Syphilis
- C . AIDS
- D . the common cold
B
Explanation:
Genital warts are caused by the Human papillomavirus. AIDS is a consequence of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. The common cold is also a viral infectious disease. Syphilis, however, is the result of a bacterial infection.
The rhythm of the heart is set by the:
- A . AV node
- B . SA node
- C . purkinje fibers
- D . Heart valves
B
Explanation:
The sinoatrial node (SA) is the main pacemaker of the heart, often initiating cardiac contraction due to generating impulses faster than other pacemaker areas. The SA is referred to as the primary pacemaker.
The heart will automatically stop if the SA node stops working:
True or False?
- A . True
- B . False
B
Explanation:
Although the SA node is the primary pacemaker of the heart, in the absence of its operation, the AV node will take over at a slower pace.
Which of the following lacks mitochondria?
- A . fungi
- B . protozoan
- C . bacteria
- D . amoeba
C
Explanation:
Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes do not possess organelles (excluding the ribosomes). Bacteria are categorized as prokaryotic and consequently do not possess a mitochondria.
The liver and skeletal muscles have a high storage of: A. glycogen
B. glucagon
C. ketone bodies
D. ammonia
Explanation:
The liver and skeletal muscles are two of the major glycogen storage sites. The liver contains a high amount in order to regulate blood sugar levels. The skeletal muscles contain a high amount of glycogen in order to satisfy their energy demands.
What is the predominant source of progesterone after ovulation?
- A . the oocyte
- B . the ovary
- C . the corpus callosum
- D . the corpus luteum
D
Explanation:
Recall that the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle occurs after ovulation which occurs after the follicular phase. Progesterone saturation is highest during the luteal phase, and the corpus luteum is most responsible for this increased amount. The oocyte is an egg, which isn’t responsible for progesterone. The ovary is a source of progesterone, but not the primary source. And the corpus callosum is the point of juncture between the hemispheres of the brain.
Which of the following is necessary for the penetration of an egg?
- A . the flagellum
- B . mitochondria
- C . acrosome
- D . centriole
C
Explanation:
In order to penetrate an egg, a spermatozoon must bind with the exterior of the egg. This binding takes place by way of the acrosome reaction, in which the sperm penetrates the jelly coat of the egg to breach and fuse with the egg plasma membrane before releasing its constituents into the eggs cytoplasm.
Which is the most inferior structure?
- A . stomach
- B . sigmoid colon
- C . pancreas
- D . small intestine
B
Explanation:
Inferior refers to the area nearest the feet. Its opposite is superior, which refers to the area nearest the top of the head. In this case, the stomach is superior to both the pancreas and the small intestine which are both superior to the sigmoid colon. The sigmoid colon is nearest the feet of the options.
Which hormone is released after a meal high in carbohydrates?
- A . insulin
- B . glucagon
- C . EPO
- D . ghrelin
A
Explanation:
When the blood stream is over saturated with glucose (as a result of a meal high in carbohydrates), the pancreas releases insulin in order to regulate the glucose levels in the blood.
Which of the following does NOT happen during inflammation?
- A . release of histamine
- B . an increase of local temperature
- C . migration of leukocytes
- D . constriction of blood vessels
D
Explanation:
Inflammation causes dilation, not constriction of blood vessels. This dilation of blood vessels is designed to increase permeability across the blood vessels and facilitate mobility of white blood cells and other phages.
Which of the following is NOT a result of sympathetic stimulation?
- A . increase in blood pressure
- B . increase of blood flow to intestines
- C . increase in blood flow to the brain
- D . dilation of pupils
B
Explanation:
Sympathetic stimulation, associated with the fight-or-flight response, results in an increased blood pressure to help the body deal with a stressful situation. The body diverts blood away from digestion and the digestive system in favor of the skin, the muscles, and the brain.
A virus contains all of the following except?
- A . mitochondria
- B . RNA
- C . amino acids
- D . DNA
A
Explanation:
A virus is neither eukaryotic nor prokaryotic, but similar to prokaryotes, viruses lack organelles. They are composed primarily of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, and proteins. Viruses lack mitochondria.
Which of the following most recently evolved to its present state?
- A . pons
- B . cerebrum
- C . cerebellum
- D . medulla oblongata
B
Explanation:
The medulla oblongata and the pons make up the brain stem, which evolved earliest. The cerebellum evolved next, followed by the cerebrum.
The oxidation of NADH occurs in which of the following?
- A . glycolysis
- B . TCA cycle
- C . ETC
- D . photosynthesis
C
Explanation:
NADH is the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and contains an electron that can be donated in the ETC. In the ETC, NADH is oxidized to NAD+.
Why does the lactic acid pathway predominate in anaerobic respiration?
- A . because the lactic acid can be made into oxygen when needed
- B . because O2 is needed for the creation of NADH
- C . because O2 is required for glycolysis
- D . without O2 there is no electron acceptor for the ETC
D
Explanation:
Lactic acid fermentation, a method of anaerobic respiration, is relied upon to generate energy for cells in the absence of oxygen.
However, because oxygen acts as the primary electron acceptor in aerobic respiration, the lactic acid pathway, lacking oxygen, contains no electron acceptor in the process.
Which pathway accounts for the least amount of ATP generated (by the pathway)?
- A . glycolysis
- B . TCA cycle
- C . ETC
- D . all have an equal number of ATP made
B
Explanation:
The generation of most to least ATP is as follows: ETC, which can produce 32 ATP; Glycolysis, which produces 2 ATP, and the TCA cycle, which produces 2 GTP in addition to electron carriers that are used in the ETC to generate ATP.
An action potential would travel fastest in:
- A . unmyelinated, thick axon
- B . myelinated, thick axon
- C . unmyelinated, thin axon
- D . myelinated thin axon
B
Explanation:
Axons are thin or thick bundles of nerve fibers. The thicker an axon is, the more quickly an action potential will travel through it. Additionally, a myelin sheath functions as an insulator that also facilitates the rapid transmission of an action potential.
Where is the ETC located in bacteria?
- A . mitochondria
- B . Golgi apparatus
- C . peroxisome
- D . plasma membrane
D
Explanation:
Eukaryotes house the ETC in their mitochondria, but bacteria, which are prokaryotic, do not possess mitochondria or organelles. The ETC in prokaryotic bacteria is located along the cell membrane.
Which of the following is NOT made by the pituitary gland?
- A . ACTH
- B . ADH
- C . FSH
- D . LH
B
Explanation:
The list of hormones made by the pituitary gland can be recalled with the mnemonic FLATPOG, signifying: FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, GH, MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone), and prolactin. ADH is made by the hypothalamus and is only secreted by the posterior pituitary.
Which of the following is found in the plasma membrane of a cell?
- A . phospholipid
- B . glycoprotein
- C . cholesterol
- D . all of the above
D
Explanation:
The plasma membrane of a cell is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, a double layer of lipids combined with phosphate groups. The hydrophilic nature of the phosphate heads and the hydrophobic nature of the lipids create a double-sided membrane with phosphates on both sides and lipids trapped between. Cholesterol and glycoprotein molecules are embedded inside the phospholipid bilayers.
Which of the following should be added to denature a protein all the way back to primary structure?
- A . reducing agent
- B . oxidizing agent
- C . water
- D . ether
A
Explanation:
In order to denature proteins to their primary structure, a reducing agent is necessary to cleave the disulfide bonds in protein’s secondary structure.
What is the role of a nurse cell?
- A . secrete testosterone
- B . secrete sperm
- C . nurture maturing red blood cells
- D . activate sperm motility
C
Explanation:
Nurse cells aid in the maturation of red blood cells. They are macrophages that absorb immature red blood cells and facilitate the growth of red blood cells.
The breakdown of a disaccharide releases energy which is stored as ATP. This is an example of a(n):
- A . Thermodynamic reaction
- B . Exothermic reaction
- C . Combination reaction
- D . Replacement reaction
- E . Endothermic reaction
B
Explanation:
An exothermic reaction releases energy, whereas an endothermic reaction requires energy. The breakdown of a chemical compound is an example of a decomposition reaction (AB C> A + B). A combination reaction (A + B C> AB) is the reverse of a decomposition reaction, and a replacement (displacement) reaction is one where compound breaks apart and forms a new compound plus a free reactant (AB + C C>AC + B or AB + CD C> AD + CB).
Which of the following molecules is thought to have acted as the first enzyme in early life on earth?
- A . Protein
- B . RNA
- C . Triglycerides
- D . Phospholipids
- E . DNA
B
Explanation:
Some RNA molecules in extant organisms have enzymatic activity; for example, the formation of peptide bonds on ribosomes is catalyzed by an RNA molecule. This and other information have led scientists to believe that the most likely molecules to first demonstrate enzymatic activity were RNA molecules.
In photosynthesis, high-energy electrons move through electron transport chains to produce ATP and NADPH.
Which of the following provides the energy to create high energy electrons?
- A . O2
- B . Light
- C . Water
- D . NADP+
- E . NADH
B
Explanation:
Electrons trapped by the chlorophyll P680 molecule in photosystem II are energized by light. They are then transferred to electron acceptors in an electron transport chain.
Cyanide is a poison that binds to the active site of the enzyme cytochrome c and prevents its activity. Cyanide is a(n):
- A . Prosthetic group
- B . Cofactor
- C . Reverse regulator
- D . Coenzyme
- E . Inhibitor
E
Explanation:
Enzyme inhibitors attach to an enzyme and block substrates from entering the active site, thereby preventing enzyme activity. As stated in the question, cyanide is a poison that irreversibly binds to an enzyme and blocks its active site, thus fitting the definition of an enzyme inhibitor.
The synaptonemal complex is present in which of the following phases of the cell cycle?
- A . Telophase of meiosis I
- B . Metaphase of meiosis II
- C . Metaphase of meiosis I
- D . Metaphase of mitosis
- E . Telophase of meiosis II
A
Explanation:
The synaptonemal complex is the point of contact between homologous chromatids. It is formed when nonsister chromatids exchange genetic material through crossing over. Once meiosis I has completed, crossovers have resolved and the synaptonemal complex no longer exists. Rather, sister chromatids are held together at their centromeres prior to separation in anaphase II.
Leaves have parallel veins: A. Monocots
B. Nonvascular plants
C. Gymnosperms
D. Dicots
E. Angiosperms
Explanation:
Monocots differ from dicots in that they have one cotyledon, or embryonic leaf in their embryos. They also have parallel veination, fibrous roots, petals in multiples of three, and a random arrangement of vascular bundles in their stems.
In ferns, the joining of egg and sperm produces a zygote, which will grow into the:
- A . Gametophyte
- B . Sporophyte
- C . Seedling
- D . Sporangium
- E . Spore
B
Explanation:
In ferns, the mature diploid plant is called a sporophyte. Sporophytes undergo meiosis to produce spores, which develop into gametophytes, which produce gametes.
The structure in which microspores are produced:
- A . 3
- B . 1
- C . 5
- D . 4
- E . 2
E
Explanation:
Anthers produce microspores (the male gametophytes of flowering plants), which undergo meiosis to produce pollen grains.
The structures composed solely of diploid cells:
- A . 1, 2, and 3
- B . 3, 4, and 5
- C . 1, 4, and 5
- D . 2, 3, and 4
- E . 1, 2, and 4
B
Explanation:
In flowering plants, the anthers house the male gametophytes (which produce sperm) and the pistils house the female gametophytes (which produce eggs). Eggs and sperm are haploid. All other tissues are solely diploid.
Which of the following processes is an example of positive feedback?
- A . High blood glucose levels stimulate insulin release, which makes muscle and liver cells take in glucose
- B . Low blood oxygen levels stimulate erythropoietin production which increases red blood cell production by bone marrow
- C . High CO2 blood levels stimulate respiration which decreases blood CO2 levels
- D . Low blood calcium levels stimulate parathyroid hormone release from the parathyroid gland. Parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from bones.
- E . Increased nursing stimulates increased milk production in mammary glands
E
Explanation:
In a positive feedback loop, an action intensifies a chain of events that, in turn, intensify the conditions that caused the action beyond normal limits. Nursing stimulates lactation, which promotes nursing. Contractions during childbirth, psychological hysteria, and sexual orgasm are all examples of positive feedback.
In which of the following stages of embryo development are the three primary germ layers first present?
- A . Blastula
- B . Zygote
- C . Gastrula
- D . Coelomate
- E . Morula
C
Explanation:
The gastrula is formed from the blastocyst, which contains a bilayered embryonic disc. One layer of this disc’s inner cell mass further subdivides into the epiblast and the hypoblast, resulting in the three primary germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm).
In the food chain below, vultures represent grass C> cow C> wolf C> vulture:
- A . Scavengers
- B . Primary carnivores
- C . Detritivores
- D . Secondary consumers
- E . Herbivores
A
Explanation:
Vultures eat carrion, or dead animals, so they are considered scavengers. Detritivores are heterotrophs that eat decomposing organic matter such as leaf litter. They are usually small.
A population of 1000 individuals has 110 births and 10 deaths in a year. Its growth rate (r) is equal to:
- A . 0.01 per year
- B . 0.11 per year
- C . 0.1 per year
- D . 0.09 per year
- E . 0.009 per year
C
Explanation:
The growth rate is equal to the difference between births and deaths divided by population size.
When a population reaches its carrying capacity?
- A . The population size begins to decrease.
- B . The population growth rate approaches zero.
- C . Other populations will be forced out of the habitat.
- D . Density-independent factors no longer play a role.
- E . Density-dependent factors no longer play a role.
B
Explanation:
Within a habitat, there is a maximum number of individuals that can continue to thrive, known as the habitat’s carrying capacity. When the population size approaches this number, population growth will stop.
Darwin’s idea that evolution occurs by the gradual accumulation of small changes can be summarized as:
- A . Convergent evolution
- B . Adaptive radiation
- C . Punctuated equilibrium
- D . Phyletic gradualism
- E . Sympatric speciation
D
Explanation:
Phyletic gradualism is the view that evolution occurs at a more or less constant rate. Contrary to this view, punctuated equilibrium holds that evolutionary history consists of long periods of stasis punctuated by geologically short periods of evolution. This theory predicts that there will be few fossils revealing intermediate stages of evolution, whereas phyletic gradualism views the lack of intermediate-stage fossils as a deficit in the fossil record that will resolve when enough specimens are collected.
At two independently assorting loci, a man has the following genotype: GgHH. He marries a woman with the genotype ggHh.
What is the probability that they will have a child who has the same genotype as the father?
- A . 0
- B . 1/2
- C . 1/4
- D . 1/8
C
Explanation:
This is a “probability” genetics question that can be answered by practical application of Mendel’s Laws. Mendel’s Law of Segregation states that alleles segregate during meiosis, resulting in gametes that carry only one allele for any given inherited trait (i.e., haploid gametes). Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment states that unlinked genes assort independently during meiosis. By applying Mendel’s Laws, we can conclude that each parent in the problem can produce two possible gametes. The father can produce the gametes GH and gH, and the mother can produce the gametes gH and gh. The probability of the father’s genotype (GgHH) appearing in the progeny can be determined by calculating the number of different gamete combinations that will produce this genotype. Thus, a GgHH zygote can only be produced by the fusion of a GH gamete and a gH gamete. The probability that one parent will donate a particular gamete is independent of the probability that the other parent will donate a particular gamete. Thus, the probability of the father donating a GH gamete is 1/2, and the probability of the mother donating a gH gamete is 1/2. The probability of producing a genotype that requires the occurrence of both these independent events is equal to the product of the individual probabilities that these events will occur. Thus, 1/2 × 1/2 = 1/4, so the probability that this couple will have a child with the genotype GgHH is 1/4.
In a certain genetically stable population, the frequency of a recessive allele (for a trait with two alleles) is 0.6.
What is the frequency of individuals expressing the dominant trait?
- A . 0.64
- B . 0.36
- C . 0.24
- D . 0.16
A
Explanation:
The question stem asks you to determine the frequency of individuals expressing the dominant trait in a genetically stable population. However, before you do that, you need to determine the allelic frequencies in the population. This question involves a practical application of the Hardy-Weinberg equation. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium states that within a genetically stable population, the gene frequencies of dominant and recessive alleles will not change over time. Two mathematical expressions are associated with the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The first relationship, p + q = 1, describes the relative allelic frequencies in a population. p is defined as the frequency of the dominant allele and q is defined as the frequency of the recessive allele, and the sum of both those frequencies adds up to 1, or 100%. The second relationship, p2 + 2pq+ q2 = 1, describes the relative genotypic frequencies in the population. p2 represents homozygous, or dominant pp genotypes; q2 represents homozygous, or frequency of the dominant allele, p, by the mathematical relationship p + q = 1. Therefore, the frequency of p is 0.4 because 0.6 + 0.4 = 1. Next, you need to determine the frequency of individuals expressing the dominant trait by recessive qq genotypes; and 2pq represents the frequency of heterozygotes, or hybrids.applying the second relationship, p2 + 2pq+ q2 = 1. The individuals expressing the dominant trait are those that have the pp and pq genotypes, so to find the total frequency of individuals expressing the dominant trait, you add p2 and 2pq. Thus, p2 = 0.4 × 0.4, or 0.16 and 2pq = 2 × 0.6 × 0.4, or 0.48. If you add the two together, you get 0.16 + 0.48, or 0.64. Thus, 0.64 is the correct frequency of individuals expressing the dominant trait.
What is the inheritance pattern of the observed trait indicated by the pedigree below?
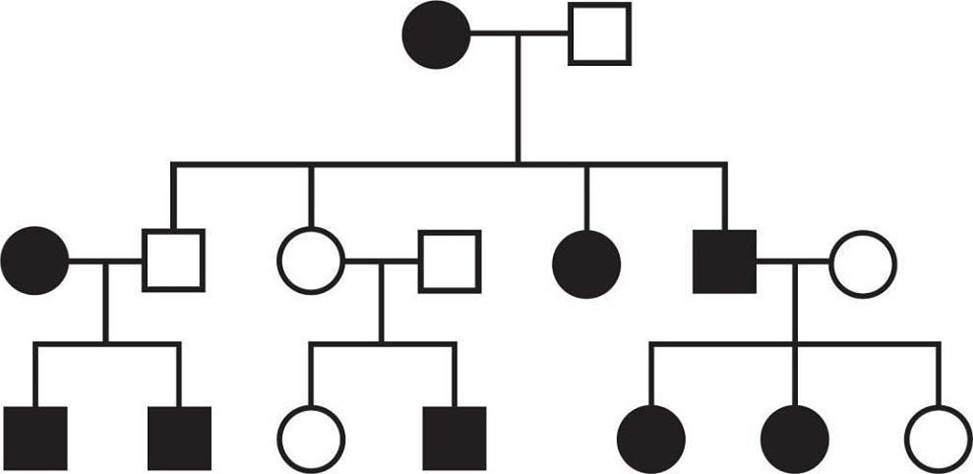
- A . Autosomal recessive
- B . Autosomal dominant
- C . X-linked recessive
- D . X-linked
- E . Cannot be determined
A
Explanation:
Pedigrees show the distribution of a single observable trait, or phenotype, across a family tree. In classical genetics, each phenotype is determined by a combination of two alleles contributed by two copies of the same (but not necessarily identical) chromosome. One allele is generally dominant, meaning it is expressed if it is present at all. In contrast, the other allele is recessive, meaning it is only expressed in the absence of a dominant allele, which generally means two copies need to be inherited to display the recessive phenotype. The exceptions are those alleles found on the X chromosome in males; males’ sex chromosomes include only one X (and one Y), so each trait coded for on the X chromosome is determined by only one allele instead of a combination of two alleles. This means it’s statistically more likely for males to inherit recessive X-linked traits since only one copy of the recessive alleles needs to be inherited to display the recessive phenotypes, as opposed to the usual two.
The fastest way to determine which inheritance pattern is shown by a pedigree, then, is to use the Kaplan shortcut: Identify whether two matching parents have an opposite offspring. If two affected parents have an unaffected offspring, both parents must have been heterozygous (having one of each allele), and the trait must be dominant: Rr × Rr C> rr. If two unaffected parents have an affected offspring, both parents must have one again been heterozygous, but in that situation, the trait being tracked must have been the recessive one: Rr × Rr C> rr. In the pedigree provided in this question, generational skipping occurs in the middle portion: Generation 2 has two unaffected parents, but generation 3 has an affected offspring. This indicates a recessive trait. Since a roughly equal number of males and females are affected (5 : 4 ratio), this is an autosomal trait.
When blood flow to human tissue is interrupted, the lack of sufficient blood supply is called ischemia. If ischemia is not restored quickly, the affected tissue may undergo a process called infarction, which involves a series of chemical changes that damage the tissue. The lack of blood supply results in lack of oxygen, and thus lactic acidosis. Mitochondrial dysfunction results. Microscopic examination and chemical analysis of ischemic cells reveal membrane degeneration, excessive calcium (Ca+) inside the cell, and free radical formation, accompanied by a reactive inflammation and free fatty acid formation. A research experiment is designed to evaluate the response of infarcted tissue to intra-arterial administration of an antioxidant. Preliminary results demonstrate that follow-up evaluation of tissue exposed to intra-arterial antioxidant injection resulted, on average, in a smaller area of infarcted tissue after seven days when compared to controls without exposure to the antioxidant. It was noted that 70% of the patients who demonstrated smaller areas of infarction also had a notable decease in edema of the ischemic tissue lasting about 6 to 10 hours after injection.
What is a possible explanation for the relationship among antioxidant injection, edema, and tissue damage?
- A . Antioxidants produce anti-infarction biochemical reactions that decrease the size of the infarct.
- B . Antioxidants decrease tissue damage by decreasing edema.
- C . The prevention of tissue damage may be produced by a combination of the effect of decreased edema and the injection of antioxidants.
- D . Increased blood flow causes paradoxical tissue damage due to ischemia.
C
Explanation:
The experimental results do not demonstrate or prove that the antioxidant is responsible for the decrease in edema or that edema is the cause of tissue damage. However, because patients exposed to the antioxidant had a smaller area of infarcted tissue, it appears that the antioxidant has a beneficial effect. Most, but not all, of the patients with smaller areas of infarct also had decreased edema, suggesting that edema may also play a role. This suggests that some type of combination of the presence of edema and antioxidants was at play when decreased tissue damage was observed. There was no measured relationship to blood flow. It is unclear exactly why the antioxidant injected samples showed deceased damage, and it is a leap to suggest that the antioxidants themselves produce chemicals or biochemical reactions that decreased the size of the infarct or the edema.
When blood flow to human tissue is interrupted, the lack of sufficient blood supply is called ischemia. If ischemia is not restored quickly, the affected tissue may undergo a process called infarction, which involves a series of chemical changes that damage the tissue. The lack of blood supply results in lack of oxygen, and thus lactic acidosis. Mitochondrial dysfunction results. Microscopic examination and chemical analysis of ischemic cells reveal membrane degeneration, excessive calcium (Ca+) inside the cell, and free radical formation, accompanied by a reactive inflammation and free fatty acid formation. A research experiment is designed to evaluate the response of infarcted tissue to intra-arterial administration of an antioxidant. Preliminary results demonstrate that follow-up evaluation of tissue exposed to intra-arterial antioxidant injection resulted, on average, in a smaller area of infarcted tissue after seven days when compared to controls without exposure to the antioxidant. It was noted that 70% of the patients who demonstrated smaller areas of infarction also had a notable decease in edema of the ischemic tissue lasting about 6 to 10 hours after injection.
How could lactic acid production and free fatty acid formation contribute to organelle dysfunction?
- A . The acidity of these molecular products, when uncorrected, alters the cell’s pH beyond that which the cell can compensate for. Organelles, containing proteins, denature as a result.
- B . Lactic acid production and free fatty acid formation function like free radicals, altering the structure of the molecular components of the organelles.
- C . Lactic acids and free fatty acids crowd the organelles within the cells, preventing them from communicating with each other in the cytoplasm.
- D . Lactic acids and free fatty acids are hydrophobic and thus can enter the membranes of the organelles, disrupting their function.
A
Explanation:
In small quantities, lactic acids and free fatty acids are tolerable due to the cell’s ability to buffer mild pH changes. However, in an ischemic setting, the cell cannot correct the pH changes, and thus the proteins that form the structural and functional components of the organelles begin to denature. Lactic acids and free fatty acids are acidic, meaning that they contribute hydrogen atoms to the environment, whereas free radicals are deficient in electrons. Although the volume of acidic molecules within the cell is not beneficial for the organelles, their pH is their most harmful characteristic and thus the most immediately damaging consequence. Free fatty acids are hydrophobic and thus may be able to pass through organelle membranes, but they cause organelle dysfunction from outside the organelle in the cytoplasm as well.
When blood flow to human tissue is interrupted, the lack of sufficient blood supply is called ischemia. If ischemia is not restored quickly, the affected tissue may undergo a process called infarction, which involves a series of chemical changes that damage the tissue. The lack of blood supply results in lack of oxygen, and thus lactic acidosis. Mitochondrial dysfunction results. Microscopic examination and chemical analysis of ischemic cells reveal membrane degeneration, excessive calcium (Ca+) inside the cell, and free radical formation, accompanied by a reactive inflammation and free fatty acid formation. A research experiment is designed to evaluate the response of infarcted tissue to intra-arterial administration of an antioxidant. Preliminary results demonstrate that follow-up evaluation of tissue exposed to intra-arterial antioxidant injection resulted, on average, in a smaller area of infarcted tissue after seven days when compared to controls without exposure to the antioxidant. It was noted that 70% of the patients who demonstrated smaller areas of infarction also had a notable decease in edema of the ischemic tissue lasting about 6 to 10 hours after injection.
Which of the following chemical moieties forms the backbone of DNA?
- A . Nitrogenous bases
- B . Glycerol
- C . Amino groups
- D . Pentose and phosphate
D
Explanation:
DNA is composed of nucleotides joined together in long chains. Nucleotides are composed of a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The bases form the “rungs” of the ladder at the core of the DNA helix and the pentose-phosphates are on its outside, or backbone.
Which of the following organelles helps green plants synthesize organic compounds like starch in the presence of sunlight?
- A . Mitochondria
- B . Chloroplast
- C . Ribosomes
- D . Golgi body
B
Explanation:
Green plants, with the help of sunlight and in the presence of enzymes, synthesize organic compounds like starch from inorganic compounds like CO 2 and H 2 O. This is known as photosynthesis. Chloroplast is the organelle to perform photosynthesis. Plants that are devoid of chloroplast cannot synthesize starch.