OMG OMG-OCUP2-INT200 OMG Certified UML Professional 2 (OCUP 2) – Intermediate Level Online Training
OMG OMG-OCUP2-INT200 Online Training
The questions for OMG-OCUP2-INT200 were last updated at Dec 07,2025.
- Exam Code: OMG-OCUP2-INT200
- Exam Name: OMG Certified UML Professional 2 (OCUP 2) - Intermediate Level
- Certification Provider: OMG
- Latest update: Dec 07,2025
Which statements apply to arguments of interaction occurrences? (Choose two.)
- A . Arguments to interaction occurrences only apply when the corresponding interaction is value returning.
- B . The arguments may be constants (literals).
- C . An argument of an interaction occurrence must only have simple types.
- D . Arguments to interaction occurrences must always correspond to IN-parameters.
- E . The arguments may refer to parameters of the enclosing interaction.
What is the difference between a tag definition and a tagged value?
- A . The properties of metaclasses are sometimes referred to as tag definitions. When a metaclass is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tagged values.
- B . The properties of stereotypes are sometimes referred to as tagged values. When a stereotype is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tag definitions.
- C . The properties of stereotypes are sometimes referred to as tag definitions. When a stereotype is applied to a model element, the values of the properties may be referred to as tagged values.
- D . They are synonyms.
What kind of relationship is an extension in UML 2.0?
- A . generalization
- B . dependency
- C . association
- D . reification
In the exhibit, if the incoming arrows provide one control value and two data values, what values are provided to the outgoing arrows?
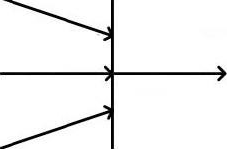
- A . the two data values
- B . a single control value
- C . a single data value combining the original two data values
- D . both the control and two data values
An encapsulated classifier is characterized by which fact?
- A . acts as a package and can own one or more classifiers
- B . hides information from other classifiers
- C . can own one or more ports
- D . has an encapsulation shell
What kinds of arrows connect to central buffers?
- A . object flows
- B . state transitions
- C . unidirectional associations
- D . control flows
- E . message passing
- F . dependencies
What does reaching the terminating pseudostate mean?
- A . The context object of the state machine is terminated.
- B . The enclosing region is completed.
- C . The final state has been reached.
- D . A completion transition has occurred.
- E . The "do" activity of the current state has completed.
What are valid ways to present a component’s artifacts file, such as a jar file? (Choose two.)
- A . stereotype of class with keyword <<file>> with a solid arrow pointing to the related component
- B . stereotype of class with keyword <<archive>> with a dashed arrow pointing to the related component
- C . stereotype of a component with keyword <<archive>> with a dashed arrow pointing to the related component
- D . as a compartment of a related component
- E . stereotype of a component with keyword <<file>> with a solid arrow pointing to the related component
How many arrows can point from a flow final node?
- A . one
- B . any number
- C . none
- D . two
What is NOT a correct assertion?
- A . A model element can be extended by several stereotypes at the same time.
- B . Un-applying a profile from a model deleted stereotypes extending the model.
- C . Stereotypes extending a model element can be retracted at any time.
- D . Stereotypes extending a model element are immutable.
Latest OMG-OCUP2-INT200 Dumps Valid Version with 133 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

