Nokia 4A0-112 Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol Online Training
Nokia 4A0-112 Online Training
The questions for 4A0-112 were last updated at Nov 18,2025.
- Exam Code: 4A0-112
- Exam Name: Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol
- Certification Provider: Nokia
- Latest update: Nov 18,2025
Refer to the exhibit.
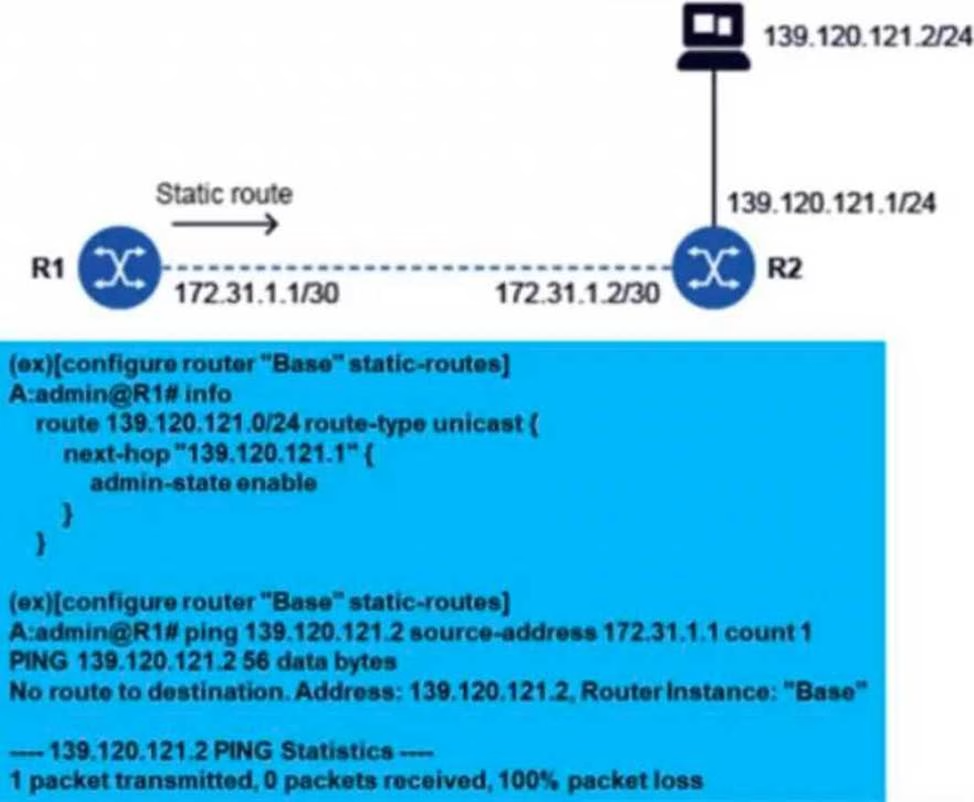
A static route has been configured on router R1 to reach the PC at 139.120.121.2.
What might be causing the ping to fail?
- A . Router R2 needs a static route to the PC.
- B . Router R1 needs a static route to router R2.
- C . The configured next hop does not belong to a subnet adjacent to R1.
- D . The configured static route needs to be a default route.
Refer to the exhibit.
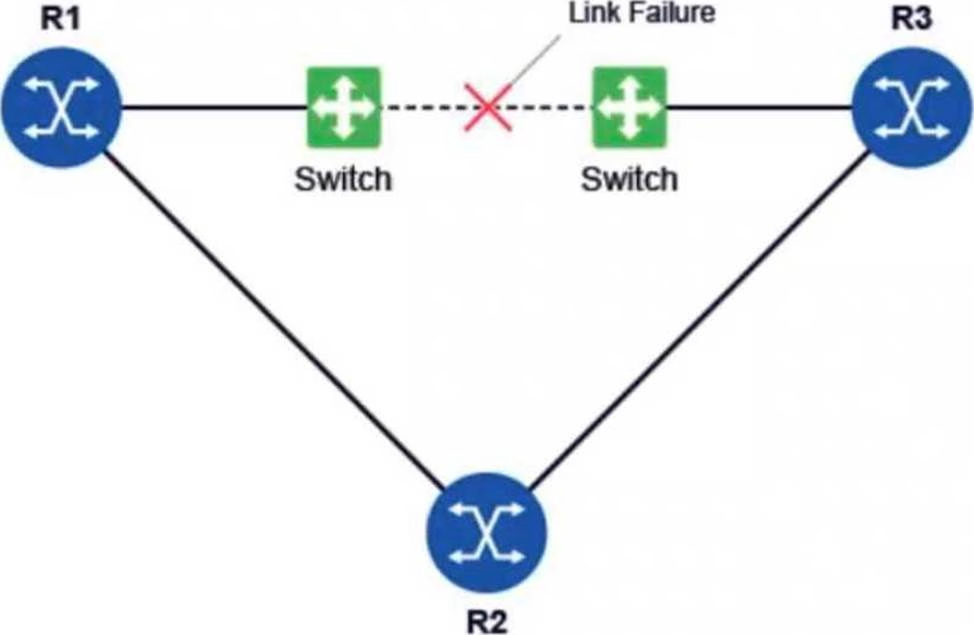
All routers in the diagram are running a link-state routing protocol. Before the link failure, all routers have operational adjacencies with each other and there is a BFD session between routers R1 and R3.
After the link failure, which of the following affects the routing protocol’s convergence time?
- A . The value of the Ethernet hello timers on the switches.
- B . The value of the routing protocol hello timers on routers R1 and R3.
- C . The value of the BFD transmit interval, receive interval and multiplier settings on routers R1 and R3.
- D . The time taken by the switches to detect that the physical ports are down.
When a router performs the SPF calculation, which router is used as the root of the shortest path tree?
- A . The router with the fewest links.
- B . The router with the lowest router ID.
- C . The router’s closest neighbor.
- D . The router doing the calculation.
A routing domain is using a single-area link-state routing protocol.
Which of the following is NOT information that a router can share with other routers in the domain using protocol-specific messages?
- A . The IP prefixes of subnets directly attached to the router.
- B . IP prefixes known by the router because it is running ad additional routing protocol.
- C . A copy of the local routing table.
- D . The local router ID and the router IDs of neighboring routers.
Refer to the exhibit.
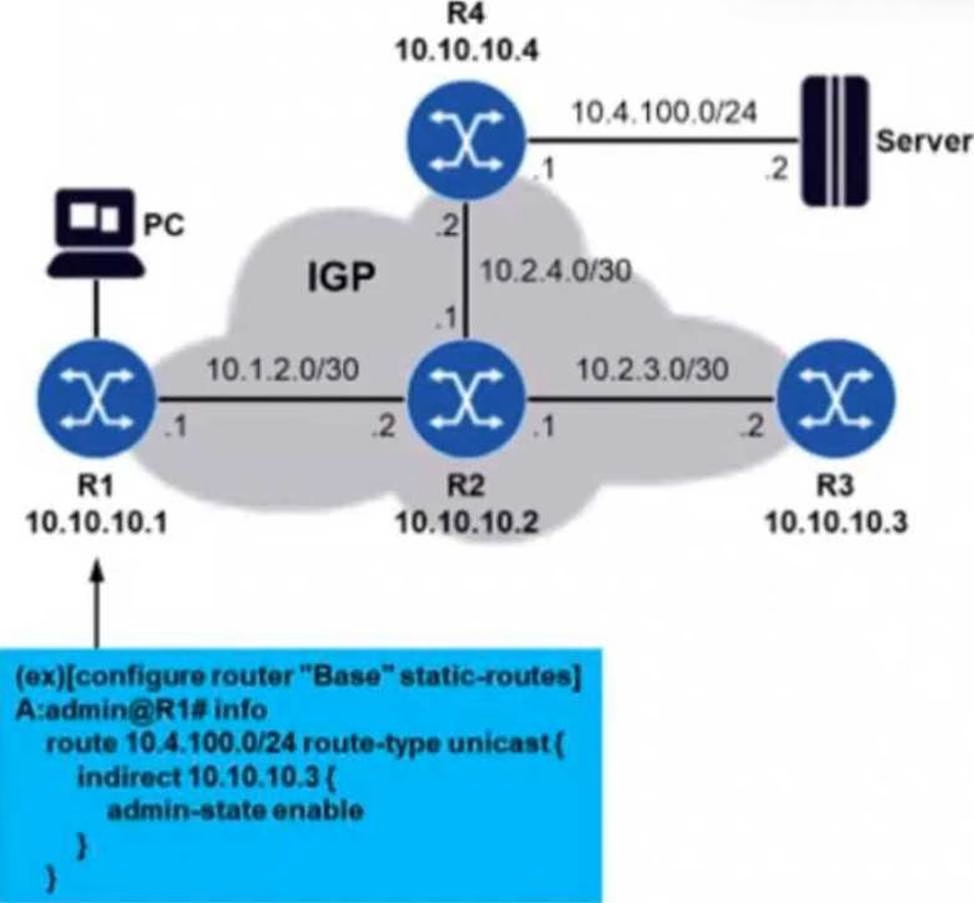
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other’s system IP addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails.
What may be the problem in this case?
- A . Router R1 drops the echo request because address 10.10.10.3 does not belong to an adjacent router.
- B . Router R2 drops the echo request because it does not have subnet 10.4.100.0/24 in its routing table.
- C . Router R3 drops the echo request because it does not have subnet 10.4.100.0/24 in its routing table.
- D . The echo request arrives at the server but there is no path for the echo response to return to router R1.
Latest 4A0-112 Dumps Valid Version with 40 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

