Cisco 350-701 Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR) Online Training
Cisco 350-701 Online Training
The questions for 350-701 were last updated at Jan 12,2026.
- Exam Code: 350-701
- Exam Name: Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies (SCOR)
- Certification Provider: Cisco
- Latest update: Jan 12,2026
What is a difference between FlexVPN and DMVPN?
- A . DMVPN uses IKEv1 or IKEv2, FlexVPN only uses IKEv1
- B . DMVPN uses only IKEv1 FlexVPN uses only IKEv2
- C . FlexVPN uses IKEv2, DMVPN uses IKEv1 or IKEv2
- D . FlexVPN uses IKEv1 or IKEv2, DMVPN uses only IKEv2
Which cloud service model offers an environment for cloud consumers to develop and deploy applications without needing to manage or maintain the underlying cloud infrastructure?
- A . PaaS
- B . XaaS
- C . IaaS
- D . SaaS
Which deployment model is the most secure when considering risks to cloud adoption?
- A . Public Cloud
- B . Hybrid Cloud
- C . Community Cloud
- D . Private Cloud
An engineer must force an endpoint to re-authenticate an already authenticated session without disrupting the endpoint to apply a new or updated policy from ISE.
Which CoA type achieves this goal?
- A . Port Bounce
- B . CoA Terminate
- C . CoA Reauth
- D . CoA Session Query
Elliptic curve cryptography is a stronger more efficient cryptography method meant to replace which current encryption technology?
- A . 3DES
- B . RSA
- C . DES
- D . AES
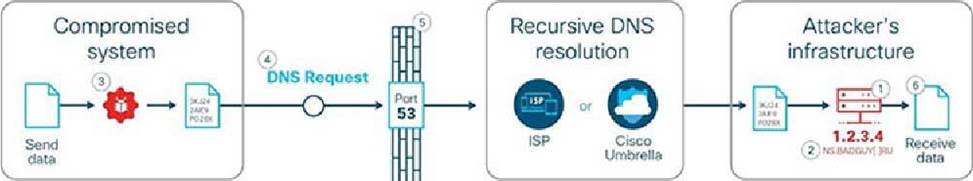
How is DNS tunneling used to exfiltrate data out of a corporate network?
- A . It corrupts DNS servers by replacing the actual IP address with a rogue address to collect information or start other attacks.
- B . It encodes the payload with random characters that are broken into short strings and the DNS server
rebuilds the exfiltrated data. - C . It redirects DNS requests to a malicious server used to steal user credentials, which
allows further damage
and theft on the network. - D . It leverages the DNS server by permitting recursive lookups to spread the attack to other DNS servers.
How is DNS tunneling used to exfiltrate data out of a corporate network?
- A . It corrupts DNS servers by replacing the actual IP address with a rogue address to collect information or start other attacks.
- B . It encodes the payload with random characters that are broken into short strings and the DNS server
rebuilds the exfiltrated data. - C . It redirects DNS requests to a malicious server used to steal user credentials, which
allows further damage
and theft on the network. - D . It leverages the DNS server by permitting recursive lookups to spread the attack to other DNS servers.
How is DNS tunneling used to exfiltrate data out of a corporate network?
- A . It corrupts DNS servers by replacing the actual IP address with a rogue address to collect information or start other attacks.
- B . It encodes the payload with random characters that are broken into short strings and the DNS server
rebuilds the exfiltrated data. - C . It redirects DNS requests to a malicious server used to steal user credentials, which
allows further damage
and theft on the network. - D . It leverages the DNS server by permitting recursive lookups to spread the attack to other DNS servers.
How is DNS tunneling used to exfiltrate data out of a corporate network?
- A . It corrupts DNS servers by replacing the actual IP address with a rogue address to collect information or start other attacks.
- B . It encodes the payload with random characters that are broken into short strings and the DNS server
rebuilds the exfiltrated data. - C . It redirects DNS requests to a malicious server used to steal user credentials, which
allows further damage
and theft on the network. - D . It leverages the DNS server by permitting recursive lookups to spread the attack to other DNS servers.
How is DNS tunneling used to exfiltrate data out of a corporate network?
- A . It corrupts DNS servers by replacing the actual IP address with a rogue address to collect information or start other attacks.
- B . It encodes the payload with random characters that are broken into short strings and the DNS server
rebuilds the exfiltrated data. - C . It redirects DNS requests to a malicious server used to steal user credentials, which
allows further damage
and theft on the network. - D . It leverages the DNS server by permitting recursive lookups to spread the attack to other DNS servers.
Latest 350-701 Dumps Valid Version with 327 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund