Based on the information shown in the exhibit, what configuration change must the administrator make to fix the connectivity issue?
Refer to the exhibit.
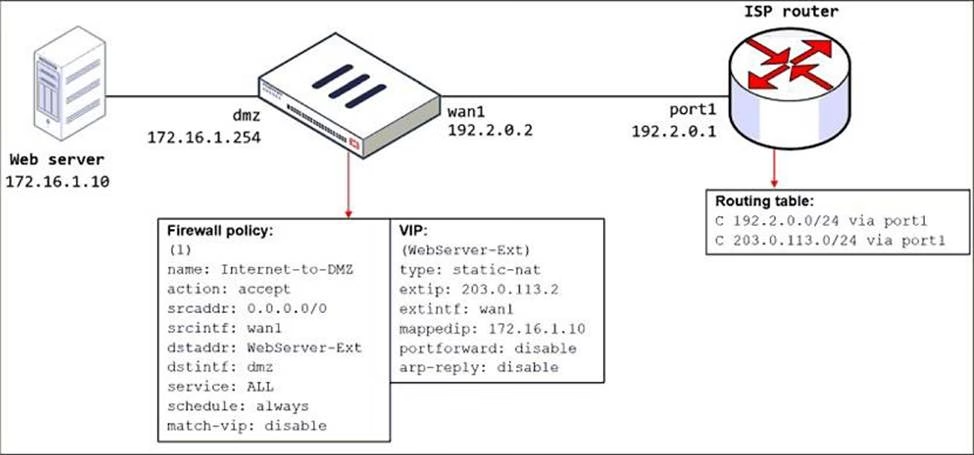
The exhibit shows a diagram of a FortiGate device connected to the network, the firewall policy and VIP configuration on the FortiGate device, and the routing table on the ISP router.
When the administrator tries to access the web server public address (203.0.113.2) from the internet, the connection times out. At the same time, the administrator runs a sniffer on FortiGate to capture incoming web traffic to the server and does not see any output.
Based on the information shown in the exhibit, what configuration change must the administrator make to fix the connectivity issue?
A . Configure a loopback interface with address 203.0.113.2/32.
B . In the VIP configuration, enable arp-reply.
C . Enable port forwarding on the server to map the external service port to the internal service port.
D . In the firewall policy configuration, enable match-vip.
Answer: B
Explanation:
In the routing table of the ISP we can see that the route is C (connected) which means that if there is no
ARP entry, traffic will be dropped by the ISP, and this is why there is no packets in the forti sniffer.
The external interface address is different from the external address configured in the VIP. This is not a problem as long as the upstream network has its routing properly set. You can also enable ARP reply on the VPN (enabled by default, here disabled) to facilitate routing on the upstream network.
Enabling ARP reply is usually not required in most networks because the routing tables on the adjacent devices contain the correct next hop information, so the networks are reachable. However, sometimes the routing configuration is not fully correct, and having ARP reply enabled can solve the issue for you. For this reason, it’s a best practice to keep ARP reply enabled.
Latest FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 Dumps Valid Version with 200 Q&As
Latest And Valid Q&A | Instant Download | Once Fail, Full Refund

